This article will show a simple financial model for online taxi business t calculating an individual trip cost. This should be considered a template and a starting point for your taxi business. A link to a fully functional google sheet with all the formulas is attached at the end of this article.
In the subsequent sections, we will explore each part of a typical financial modal for a taxi trip.
Table of Contents
Togglefinancial model for online taxi business
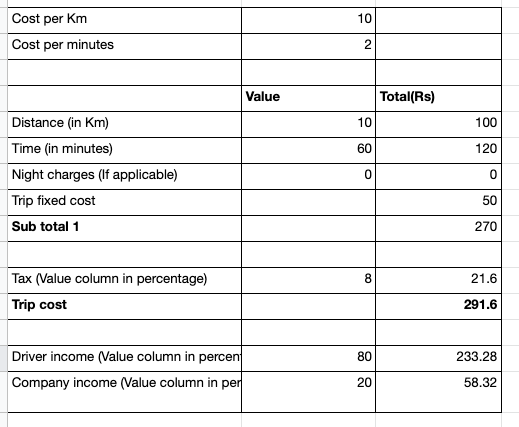
Base fare(Cost for distance and time)
As a first step to configuring a trip cost for our taxi business, we need to set the base fare for both distance and time. This fare will be set per distance(Km) and per time(minutes). According to our business plan, we need to calculate the fare(any one or both of them) for a particular trip.
For example, if a passenger travels 10km in 30 minutes, and the base fare is set as ₹10 per km and ₹10 per minute. So our trip cost would be 10km*₹10 is ₹100, 30 minutes*₹10 is ₹300, and ₹400 will be our total cost.
Fixed Cost and Night Fare
Our business model can include some fixed costs. This cost can be the cost associated with different vehicle models, traveling time, and luggage transport. By tradition, most taxi businesses have some sort of fixed cost associated with a trip. This cost will be added to the trip before taxes.
Along with Fixed cost, Night fare is also another cost that will be included with the trip in case of night travel. In many parts of the world, it is a norm for drivers to charge night bata when they usually take a long night trip. This fare is too added before the taxes.
Total Cost before taxes
Till now, Our trip cost includes distance cost(cost per km), minutes cost(cost per minute), night fare, and the fixed cost. Aggregation of all these fares is our total cost before taxes. According to your taxi business model, any additional charges can be included before this point, for example, fuel conveyance.
After this point, we will be adding the taxes to our total trip cost.
Taxes
Tax amounts vary from country to country and also according to the particular taxi business. So we will consider a hypothetical amount of 8% of our total cost. For example, if our total cost is ₹100 and 8% tax on it is ₹8, so now our grand total will be ₹108.
From this amount, we will be calculating our profit to the company as well as to the driver.
Income to the company and the driver
Now, from the total income for the trip, there will be a percentage split between the company and the driver. Usually, the ratio(for example, 80:20) will be larger towards the driver and low towards the company, this is because as a taxi business the company will profit from all the trips of all the vehicles in its fleet. But the driver’s profit will only be the trips that he drives.
So for example, if the total income of the trip after including the tax is ₹100 then based on the 80:20 ratio, ₹80 will be credited to the driver and ₹20 will be credited to the company.
Conclusion
Having a solid financial model is one of the crucial parts of running a successful taxi business. This article introduced a simple financial template that anyone can use to calculate income for a trip and customize based on their business needs. Even though most of the applications include some sort of finance module to automate this process, it is crucial to understand what is going on under the hood.
Trip cost sheet – Google sheet (https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1fxruIOAwxdfba37I-u-EWt77Dl4D-cLsMjHHSNpgQh0/edit?usp=sharing)
Our uber clone application has a highly customizable financial module catering to your business need. do check that out. Thanks.
